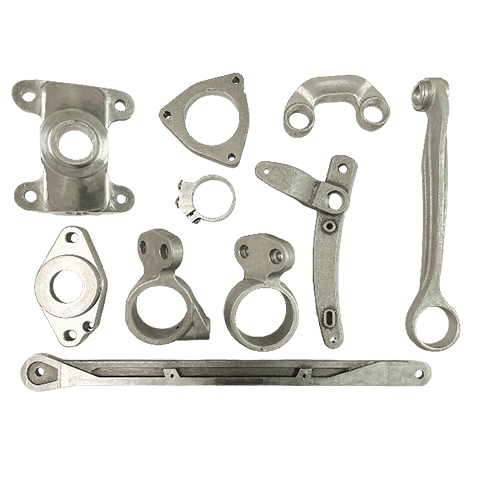
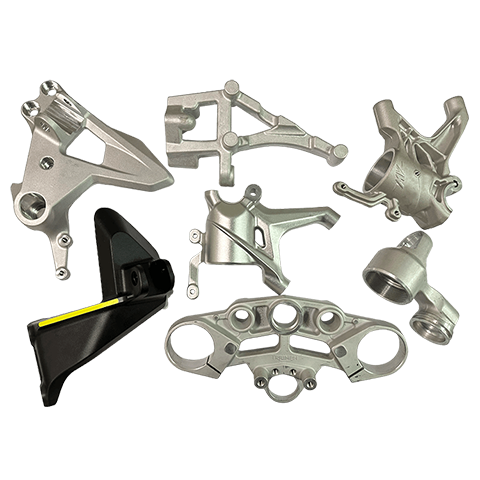
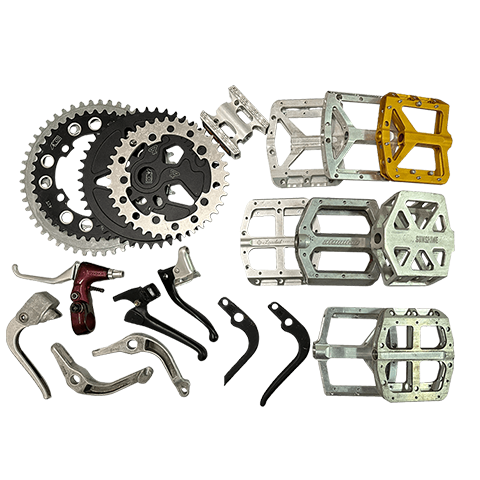
Metal Forging
Process : Solid metal → Cutting → Pre-heating → Forging → Stamping → Heat treatment → Polishing → Tumbling → Sandblasting
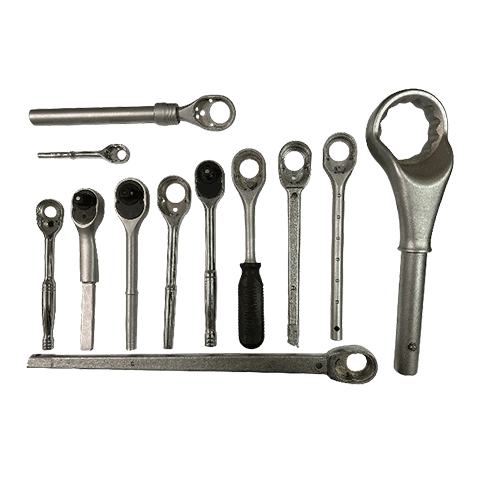
Forging is a metal shaping process that involves applying pressure to a metal workpiece using forging machinery to acheive the desired shape. It allows the metal to attain specific mechanical properties, shape, and dimensions. Depending on the forging temperature, it can be classified as hot forging (above 800℃), warm forging (300℃~800℃), or cold forging (room temperature). Hot forging is the most commonly used technique in many industries.
During the forging process, the metal undergoes deformation under applied force, which can eliminate defects such as casting porosity that may occur during the metal’s initial production stages. It retains complete metal flow lines, resulting in better mechanical performance compared to castings of the same material. Common materials used for forging include various grades of carbon steel, alloy steel, aluminum, magnesium, copper, and titanium alloys.
Advantages : Lightweight, high strength, high production efficiency, reduced subsequent processing hours, ability to produce complex-shaped parts.
Disadvantages : Higher tooling and manufacturing costs.
Applicable industries : Automotive, motorcycles, bicycles, machinery, etc.