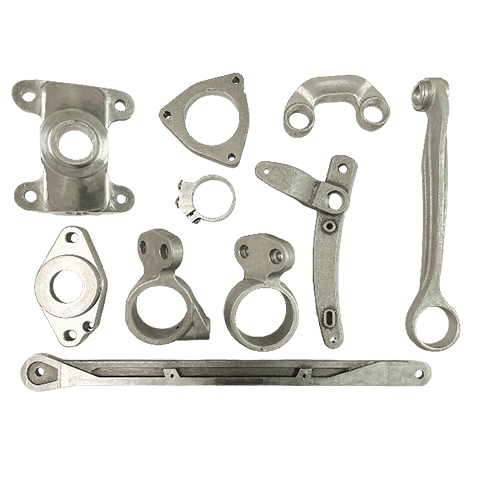
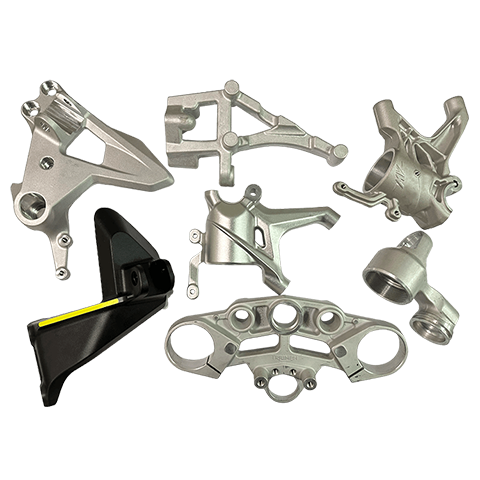
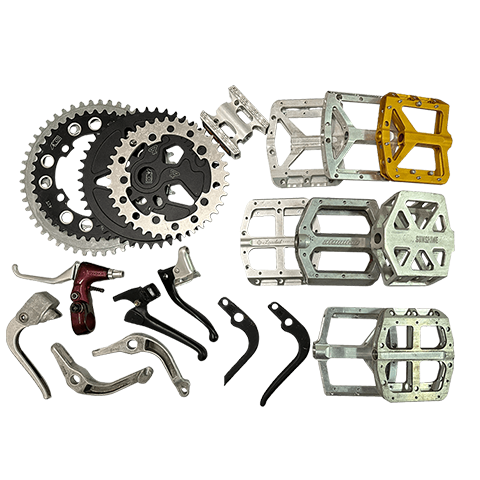
Aluminum Alloy Processing
Aluminum alloys are widely used in the automotive, motorcycle, and bicycle parts industries due to their lightweight, high strength, high ductility, excellent thermal conductivity, and ease of machining. These characteristics allow for extensive applications. Parts can be manufactured to meet specific appearance and dimensional requirements through processes such as aluminum forging, aluminum casting, gravity casting, or aluminum extrusion.
Aluminum alloys is a commonly used material in CNC machining and is also one of our areas of expertise. It is widely utilized due to its ease of cutting and milling, excellent machinability, and the availability of various alloy types. Aluminum is extensively used in industries that require lightweight and high-strength components. It is considered one of the most cost-effective metals for such applications.

Common aluminum alloys include 7075, 7050, 6082, 6063, 6061, 5754, 5083, 5052, 4140, 4130, 3004, 3003, 1100, and 1060. While they are all aluminum materials, their alloy properties are slightly different. In terms of selection, it is necessary to consider the actual application requirements. Here are some examples :
- 6061 is a high quality aluminum alloy produced through heat treatment and pre-stretching techniques, with magnesium(Mg) and silicon(Si) as the main alloying elements.
- The strength is about 2/3 of 7XXX series aluminum alloy, making it is suitable for products with general strength requirements.
- It has high toughness with good tensile and bending properties, resulting in less deformation after processing.
- Excellent machinability and weldability, making it easy to create different shapes and sizes of parts.
- Good corrosion resistance, suitable for coloring, exhibits excellent oxidation effects, and has good electroplating properties.
- 7075 is a cold-treated forging alloy with zinc as an alloying element.
- It is one of the strongest aluminum alloys and is commonly used in aerospace, automotive and military fields.
- It has lower toughness compared to other aluminum alloys, making it more prone to fracture.
- It has good machinability, but due to its high hardness, high-speed machining and careful attention to the processing temperature are required.
- Its corrosion resistance is ordinary, but it can be enhanced through surface treatment and film formation processes.
In summary, 6061 offers moderate strength and good toughness, 7075 provides extremely high strength and medium toughness, and another commonly used alloy, 6082, has properties between 6061 and 7075. Therefore, selecting the appropriate material depends on the specific application requirements such as strength, ductility, or complexity of the part. These factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance and usability of the product.
The aforementioned are common aluminum metal materials used in aluminum alloy processing. In the manufacturing of components required for various industries, the first step usually involves processing the metal materials into the desired shapes through different metal forming methods. Common forming methods include:
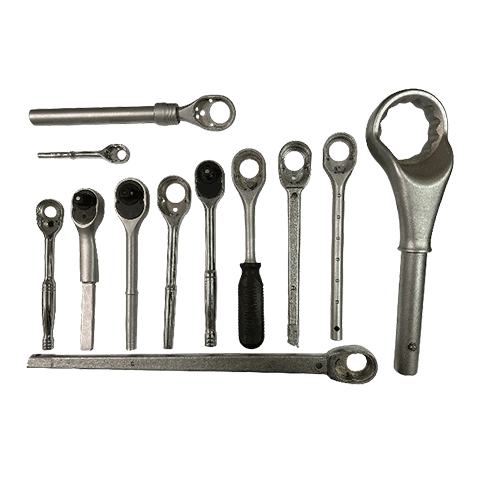
Aluminum Forgings
Process : Solid metal → Cutting → Pre-heating → Forging → Stamping → Heat treatment → Polishing → Tumbling → Sandblasting
Forging is a metal shaping process that involves applying pressure to a metal workpiece using forging machinery to acheive the desired shape. It allows the metal to attain specific mechanical properties, shape, and dimensions. Depending on the forging temperature, it can be classified as hot forging (above 800℃), warm forging (300℃~800℃), or cold forging (room temperature). Hot forging is the most commonly used technique in many industries.
During the forging process, the metal undergoes deformation under applied force, which can eliminate defects such as casting porosity that may occur during the metal’s initial production stages. It retains complete metal flow lines, resulting in better mechanical performance compared to castings of the same material. Common materials used for forging include various grades of carbon steel, alloy steel, aluminum, magnesium, copper, and titanium alloys.
Advantages : Lightweight, high strength, high production efficiency, reduced subsequent processing hours, ability to produce complex-shaped parts.
Disadvantages : Higher tooling and manufacturing costs.
Applicable industries : Automotive, motorcycles, bicycles, machinery, etc.
Aluminum Castings
Process : Molten metal → Molding → Solidifying and cooling → Cutting off → Grinding → Blasting → Heat treatment
Casting is a metal forming process where heated molten metal is poured into a mold to obtain the desired shape. It can be categorized into different casting types according to the mold and process used, such as gravity casting, die casting, low pressure casting, sand casting, lost wax casting, vacuum casting, continuous casting, etc.
Gravity Casting
It is usually used for producing large metal components like engine blocks, axles, bridges, etc. Gravity Casting is a molding method where the molten metal, under the influence of gravity, takes the desired shape within the mold. It is a type of permanent mold casting. Generally speaking, the permanent molds used in gravity casting are made of heat-resistant alloy steel, allowing for high reusability, high production efficiency, and excellent dimensional accuracy of the parts.
Due to its high thermal conductivity, large heat capacity, and fast cooling rate, parts produced through gravity casting show good casting structure, surface roughness, strength, and dimensional precision.
- Advantages : Long mold life, high precision, smooth surface, and high strength.
- Disadvantages : Higher mold cost, less suitable for small quantity production.
- Applicable industries : Automotive, motorcycle, machinery, hand tools and other parts.
Die Casting
Die casting is the most commonly used method in permanent mold casting, which uses high pressure to inject molten metal into a mold to achieve the desired shape. The metal is usually non-ferrous metal or alloy, such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, tin, and copper.This method is often employed for mass-producing thin-walled, complex, and small parts, such as automotive body components, machine parts, household appliances, casing of electronic devices, or various other components.
- Advantages : Suitable for mass production, reusable molds, fast processing speed, precise and consistent dimensions, reduced post-processing time.
- Disadvantages : Higher cost of equipment and molds, not suitable for producing small amount of diverse products.
- Applicable industries : Automotive, machinery, electronics industry.
Lost-wax Casting
Also known as investment casting, it is one of the oldest known metal forming methods. Lost-wax casting has been used in ancient civilizations such as Ancient Egypt and the Spring and Autumn period of China for casting bronze artifacts. It is a process that invests wax pattern with refractory material and a binding agent to shape a disposable ceramic mold, and then molten metal is poured into the mold to make metal castings.
Investment casting offers the advantage of producing highly complex and intricate castings with high surface smoothness. Wall thickness and internal structure can be precisely controlled during the manufacturing process. It is suitable for casting various alloys, including aluminum, magnesium, copper, steel, and different shapes and sizes of parts.
Advantages : Ability to produce parts with thin-wall, complex shapes, high surface quality, high dimensional precision, and reduce post-casting machining.
Disadvantages : Non-reusable molds, higher manufacturing costs of molds, labor-intensive.
Applicable industries : Gears, turbine blades, engine blades, medical equipment.
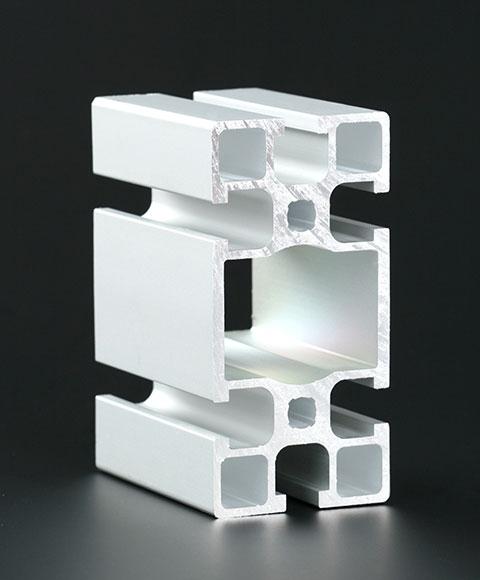
Aluminum Extrusions
Process : Solid metal → Cutting → Pre-heating → Extrusion → Straightening → Cutting → Heat Treatment
Extrusion is a hot forming method in which a metal material is continuously passed through a die with a predetermined shape at extremely high pressure and temperature, by heating, plasticizing and screw extruding, and then cooled to form the desired shape. It is typically used to produce long or continuous shape parts such as rods, tubes, strips, etc. Commonly used extruded metal materials include aluminum, copper, magnesium, titanium, lead, etc., even brittle materials can also be extruded.
Advantages : Multiple product specifications, greater production flexibility, small batch production, high dimensional accuracy, good surface quality, lower equipment cost.
Disadvantages : Large waste loss, low extrusion speed, uneven metal flow.
Applicable industries : Automotive, ships, construction, electronic industry, consumer goods, etc.