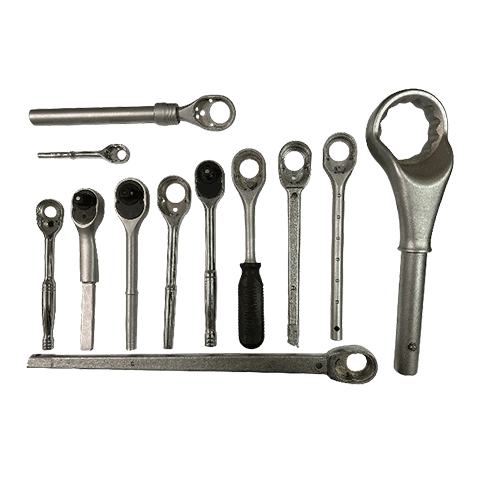
Metal Casting
Process : Molten metal → Molding → Solidifying and cooling → Cutting off → Grinding → Blasting → Heat treatment
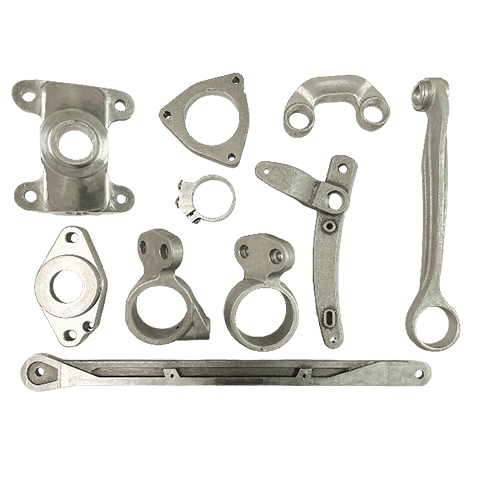
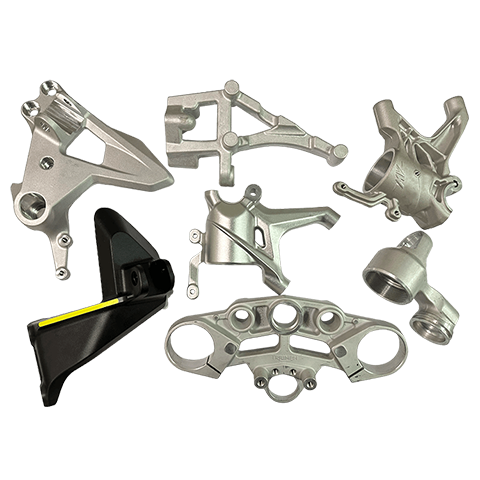
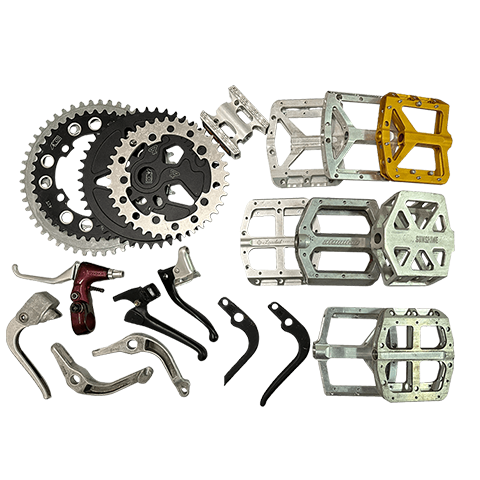
Casting is a metal forming process where heated molten metal is poured into a mold to obtain the desired shape. It can be categorized into different casting types according to the mold and process used, such as gravity casting, die casting, low pressure casting, sand casting, lost wax casting, vacuum casting, continuous casting, etc.
Gravity Casting
It is usually used for producing large metal components like engine blocks, axles, bridges, etc. Gravity Casting is a molding method where the molten metal, under the influence of gravity, takes the desired shape within the mold. It is a type of permanent mold casting. Generally speaking, the permanent molds used in gravity casting are made of heat-resistant alloy steel, allowing for high reusability, high production efficiency, and excellent dimensional accuracy of the parts.
Due to its high thermal conductivity, large heat capacity, and fast cooling rate, parts produced through gravity casting show good casting structure, surface roughness, strength, and dimensional precision.
- Advantages : Long mold life, high precision, smooth surface, and high strength.
- Disadvantages : Higher mold cost, less suitable for small quantity production.
- Applicable industries : Automotive, motorcycle, machinery, hand tools and other parts.
Die Casting
Die casting is the most commonly used method in permanent mold casting, which uses high pressure to inject molten metal into a mold to achieve the desired shape. The metal is usually non-ferrous metal or alloy, such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, tin, and copper.This method is often employed for mass-producing thin-walled, complex, and small parts, such as automotive body components, machine parts, household appliances, casing of electronic devices, or various other components.
- Advantages : Suitable for mass production, reusable molds, fast processing speed, precise and consistent dimensions, reduced post-processing time.
- Disadvantages : Higher cost of equipment and molds, not suitable for producing small amount of diverse products.
- Applicable industries : Automotive, machinery, electronics industry.
Lost-wax Casting
Also known as investment casting, it is one of the oldest known metal forming methods. Lost-wax casting has been used in ancient civilizations such as Ancient Egypt and the Spring and Autumn period of China for casting bronze artifacts. It is a process that invests wax pattern with refractory material and a binding agent to shape a disposable ceramic mold, and then molten metal is poured into the mold to make metal castings.
Investment casting offers the advantage of producing highly complex and intricate castings with high surface smoothness. Wall thickness and internal structure can be precisely controlled during the manufacturing process. It is suitable for casting various alloys, including aluminum, magnesium, copper, steel, and different shapes and sizes of parts.
Advantages : Ability to produce parts with thin-wall, complex shapes, high surface quality, high dimensional precision, and reduce post-casting machining.
Disadvantages : Non-reusable molds, higher manufacturing costs of molds, labor-intensive.
Applicable industries : Gears, turbine blades, engine blades, medical equipment.